Guava (Psidium guajava L.), often referred to as the "poor man's apple," is a highly nutritious and commercially important fruit crop grown widely across tropical and subtropical regions. Rich in vitamin C, antioxidants, dietary fibre, and minerals.
India is one of the largest producers of guava in the world, with major growing states including Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka. The total area under guava cultivation in India exceeds 300,000 hectares, with an annual production of over 4 million tonnes.
Guava holds significant importance in India due to its high nutritional value, versatility in culinary applications, and traditional medicinal uses. It's a good source of vitamin C, pectin, calcium, and phosphorus, making it valuable for processed food products like jams and jellies. Guava leaves are also used for their medicinal properties, traditionally employed for treating diarrhea, and for dyeing and tanning. Guavas are adaptable to diverse climates and soil conditions, making them a resilient and valuable crop for farmers.
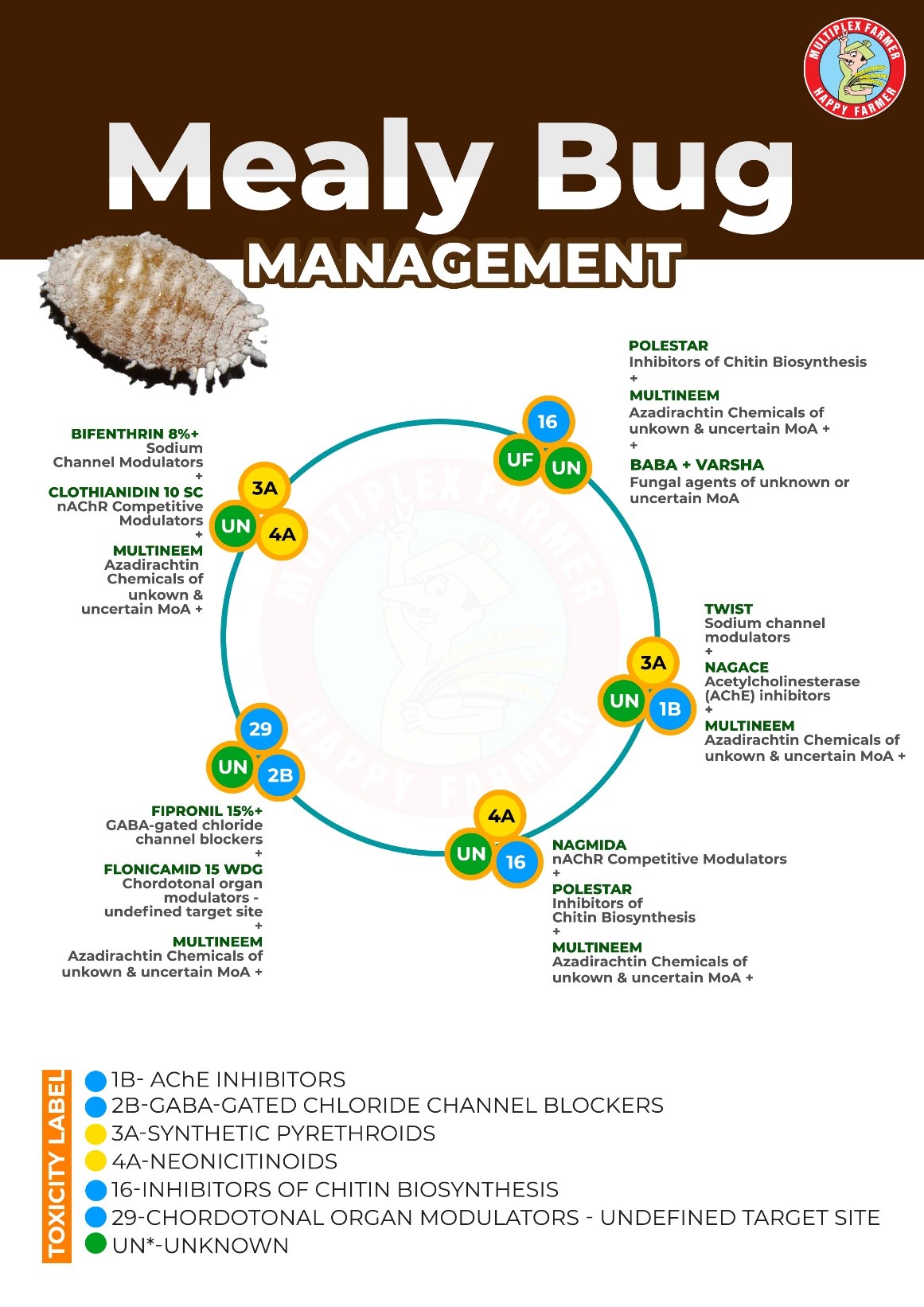
Despite its hardiness, guava is vulnerable to several pest and disease problems that can severely reduce yield and fruit quality. The guava mealybug has become increasingly problematic in recent years, especially under intensive cultivation and changing climatic conditions.
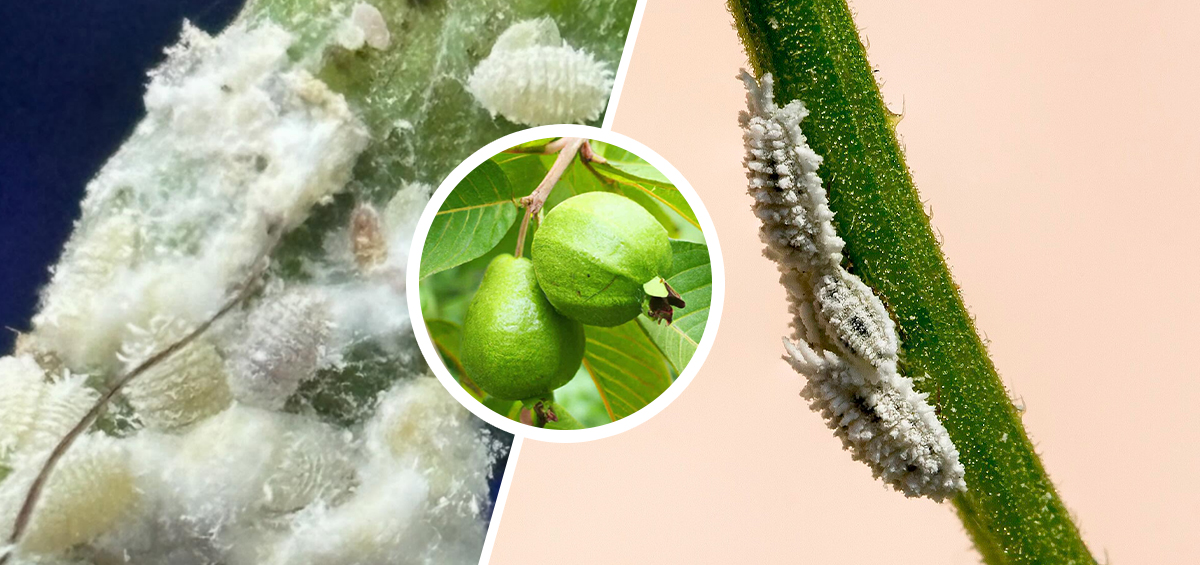
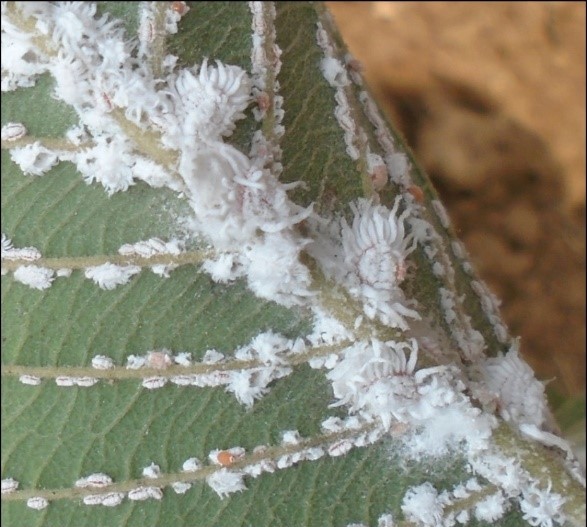
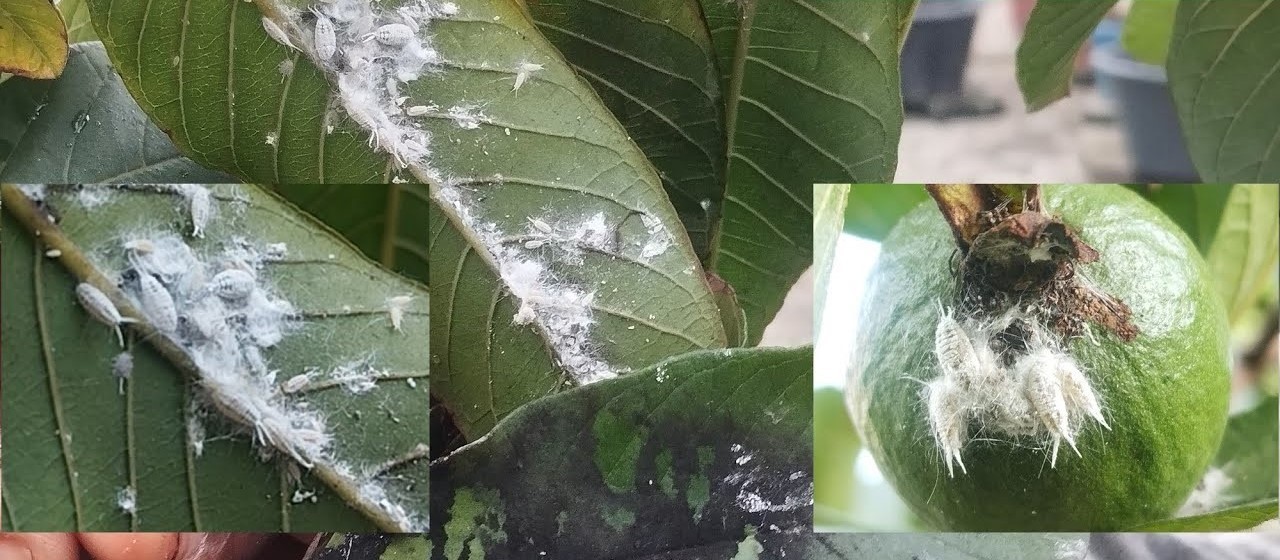
The guava mealybug (Ferrisia virgata) has emerged as a serious pest due to its polyphagous nature, ability to reproduce rapidly, and strong resistance to conventional insecticides. It not only affects guava but also infests several other horticultural and ornamental plants, making it difficult to manage in mixed cropping systems.
The Guava Mealy Bug is a soft-bodied, oval insect covered with a white waxy coating, with adult females displaying two distinctive waxy filaments at the posterior end. These insects reproduce both sexually and parthenogenetically, completing their life cycle in about 30–40 days under favourable conditions, though development slows during colder months. Females lay 350–500 orange-coloured eggs in loose, cottony ovisacs typically found on stems or leaves. Eggs hatch in 5–10 days into mobile orange crawler nymphs, with females passing through three nymphal instars and males through four nymphal instars. Adult females are pinkish and lightly covered with wax, continuing to feed and reproduce, while males are rarely observed. Generally, one generation is completed per month in optimal climates.